We are proud to announce that Hallvard F. Svendsen, Hanna K. Knuutila, Ardi Hartono, Maxime Francois and Diego Morlando at NTNU, together with external collaborators Peter Moser (RWE) and Georg Wiechers (RWE) have published a new article presenting results from the AURORA and SCOPE projects.
The publication introduces a new class-based aerosol model for the CESAR1 solvent system, providing improved insight into droplet growth and aerosol emissions during CO₂ capture. The model is validated against pilot-scale data from the RWE Niederaussem plant under operating conditions covering both low and high particle number count (PNC).
📄 Title: Understanding aerosol growth and emissions: CO2 capture in the RWE Niederaussem pilot plant using CESAR1
📚 Journal: International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control
🔬 Key findings
- Improved prediction of aerosol behavior: The model successfully predicts steady-state amine concentrations in the water wash, the composition of droplets interacting with the outlet demister, and the resulting emissions.
- Aerosols matter: Aerosols account for a significant fraction of the solvent emission—up to 92% of piperazine (PZ) and 30% of 2-amino-2-methylpropanol (AMP) under high PNC. .
- Particle number count and size effects: At low PNC, droplets grew to similar sizes regardless of initial size, while at high PNC, outlet droplet sizes depended strongly on inlet size. Larger droplets carried higher amine concentrations and higher PZ/AMP ratios than smaller ones.
- Gas phase amine depletion: Even at low PNC, aerosols reduced gas-phase amine concentrations, with PZ being much more affected than AMP.
📌 Conclusion
A new validated class-based aerosol model was developed and validated against pilot plant data at RWE Niederaussem. The model predicts well the amine emissions and provides insights into aerosol droplet size growth and amine concentration development along the absorber and water wash columns.
This approach provides a more reliable tool for designing cleaner, safer, and more efficient industrial CO₂ capture systems.
Authors:
- Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) – Department of Chemical Engineering: Diego Morlando, Ardi Hartono and Hanna K. Knuutila.
Stay tuned as AURORA continues to generate knowledge that will help make carbon capture cleaner, safer, and more cost-effective for industries across Europe.
Publication – Development of a Validated Rate-Based Model
Abstract In this work, we developed a new e-NRTL thermodynamic framework for CO2 absorption in aqueous mixtures of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) in Aspen Plus. The e-NRTL AMP/PZ/H2O/CO2 model was fitted on experimental data covering a range of AMP concentration from 12 to 48 mass % and PZ concentration…
Publication – Pilot-scale CO2 capture in a cement plant with CESAR1
Abstract Carbon capture from hard-to-abate industries is essential. This study investigates the effect of stripper pressure on the performance of amine-based CO2 capture from cement flue gas, using the CESAR1 solvent. Through a rigorous data filtering and binning methodology, experimental results were systematically categorized, enabling a precise evaluation of how…
Thermodynamic Properties of CO₂ Absorption in CESAR1 — Essential Data for Better Process Modelling
We are proud to announce a new scientific publication from the AURORA project, authored by Diego Morlando, Ardi Hartono and Hanna K. Knuutila, published in Carbon Capture Science & Technology. This important work provides extensive experimental data on the thermodynamic properties of CESAR1, a key solvent blend for industrial carbon…
Journal Publication – In-Depth Study of CESAR1 Solvent Degradation Under CO₂ Capture Conditions
A new scientific publication based on research from the AURORA project has just been released in the journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. This study delivers an in-depth analysis of the degradation behaviour of the CESAR1 solvent —a popular choice for solvent-based post-combustion CO₂ capture.This work, developed under the AURORA…
Conference publication – GHGT-17: Viscosity and Density data for the CESAR1 solvent
Abstract Global warming is a major issue that needs to be addressed and limited. The CESAR1 solvent blend has a high potential for becoming a commonly employed, commercial solvent system. In this work, the viscosity and density data for aqueous CO2 loaded CESAR1 (26.6 wt.% AMP 12.8 wt.% PZ) solution…
Conference publication – GHGT-17: “Storage potential evaluation of eastern Mediterranean area as final step of the full chainassessment”
The final step in capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions is geological storage, where CO₂ is injected deep underground into carefully chosen locations. These locations could be natural formations like saline aquifers (underground reservoirs filled with salty water) or empty oil and gas fields.This work, part of the AURORA…
Understanding Solvent Degradation in CO₂ Capture – CESAR1 Solvent Degradation in Pilot and Laboratory Scale
The fight against climate change requires innovative solutions, and one promising method is CO₂ capture and storage (CCS). CCS involves capturing carbon dioxide from industrial emissions before it reaches the atmosphere. At the heart of this process are specialized chemical solvents, such as CESAR1, which absorb CO₂ from flue gases.While…
Turning Waste Into Opportunity: Thermal Reclamation Chemistry of Common Amine Solvents
CO2 capture technology is vital for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. But what happens when the chemicals used in this process wear out or degrade? Scientists have been studying how to rejuvenate these chemicals through a method called thermal reclaiming. This research focuses on ethanolamine (MEA), a widely used solvent for…
Closing Knowledge Gaps – Density and Viscosity of Unloaded and CO2-loaded Aqueous AMP-PZ blends
AURORA’s latest scientific journal publication provides experimental density and viscosity data on different unloaded and CO2-loaded aqueous blends of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) used for absorption-based CO2 capture. The paper also provides correlations for density and viscosity suitable for various modelling works.In our previous review article, we identified knowledge…
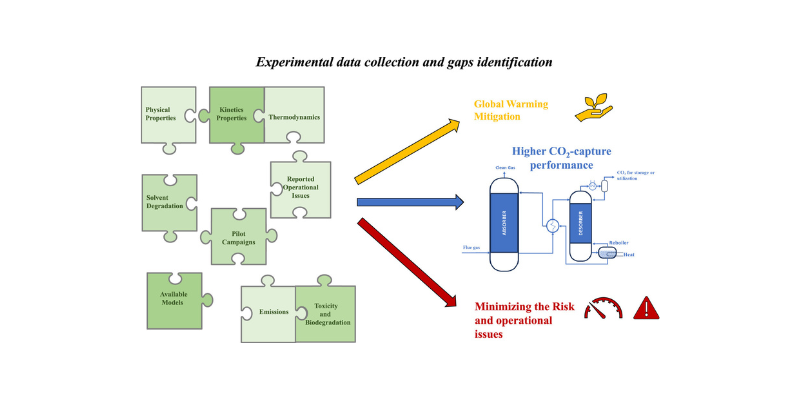
Unlocking New Potential of CESAR1-based chemical absorption Technology: Available data and knowledge gaps of the CESAR1 solvent system
AURORA latest review paper, developed in collaboration with researchers from SINTEF and NTNU, provides a comprehensive analysis of the CESAR1 solvent system. It collects and evaluates existing experimental data, highlights knowledge gaps, and outlines the necessary next steps in research to optimize the use of CESAR1 for CO₂ capture.In the…