We are proud to announce a new scientific publication from the AURORA project, authored by Diego Morlando, Ardi Hartono and Hanna K. Knuutila, published in Carbon Capture Science & Technology. This important work provides extensive experimental data on the thermodynamic properties of CESAR1, a key solvent blend for industrial carbon capture, helping to improve process modelling and energy optimization.
This important work provides extensive experimental data on the thermodynamic properties of CESAR1, a key solvent blend for industrial carbon capture, helping to improve process modelling and energy optimization.
📄 Title: Thermodynamic data for CO2 absorption in aqueous 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) solutions: CO2 solubility, N2 O solubility, heat of absorption of CO2 , pH and liquid speciation
📚 Journal: Carbon Capture Science & Technology
🌍 Why this study is important
Carbon capture is essential to reduce CO₂ emissions from industrial sources. Among available technologies, chemical absorption using aqueous amine solutions stands out as one of the most promising. The CESAR1 solvent blend, a mixture of 3 M AMP (2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol) and 1.5 M PZ (piperazine), is considered a benchmark for next-generation CO₂ capture.
However, as highlighted in earlier reviews (e.g. Morlando et al. 2024), key gaps in experimental thermodynamic data for CESAR1 have limited the accuracy of process models and the design of capture plants. This new study addresses these gaps, providing essential data needed to optimise CO2 capture plants using the CESAR1 solvent for commercial deployment.
Authors:
- Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) – Department of Chemical Engineering: Diego Morlando, Ardi Hartono and Hanna K. Knuutila.
🔬 Key contributions of the study
- CO₂ solubility data extended to high temperatures
The team measured CO₂ solubility in aqueous AMP+PZ solutions (including the CESAR1 blend) at temperatures up to 150°C, expanding the range of temperature and CO2 loading previously investigated and supporting the evaluation of high-pressure, energy-efficient stripping processes.
- Heat of absorption data
New measurements of the heat of absorption of CO₂ across various temperatures, CO₂ loadings, and amine concentration ratios offer insights into the energy required for solvent regeneration.
- N₂O solubility data for CESAR1
N2O solubility in the CESAR1 was measured at different temperatures and CO2 concentrations. These data can be used to estimate the concentration of the free CO2 in the mixed solvent, constituting an important part of the thermodynamic framework.
- Liquid speciation and pH behaviour
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) provided data on the distribution of molecular and ionic species formed during CO₂ absorption in CESAR1. The study also mapped pH behaviour across different CO₂ loadings and amine concentrations. These data contribute to a better understanding of the chemistry of the solvent system at relevant process conditions.
📌 What we learned
- AMP/PZ concentration ratios impact thermodynamic properties. While small changes in the AMP/PZ ratio had minimal impact, higher AMP/PZ concentration ratio led to behaviour closer to AMP alone.
- Heat of absorption is influenced by CO₂ loading and amine composition but is constant with temperature across the range investigated.
- N₂O solubility decreases with temperature and CO₂ loading.
- Speciation results clarified how CO₂ binds within CESAR1, helping validate reaction mechanisms for modelling.
🌱 Contribution to AURORA’s mission
This research directly supports AURORA’s mission to qualify CESAR1 for industrial-scale deployment, offering:
✅ A stronger experimental foundation for accurate process model development
✅ Data to improve the energy optimization of the process
✅ A clearer understanding of CESAR1’s chemical behaviour under operational conditions
Stay tuned as AURORA continues to generate knowledge that will help make carbon capture cleaner, safer, and more cost-effective for industries across Europe.
Journal Publication – In-Depth Study of CESAR1 Solvent Degradation Under CO₂ Capture Conditions
A new scientific publication based on research from the AURORA project has just been released in the journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. This study delivers an in-depth analysis of the degradation behaviour of the CESAR1 solvent —a popular choice for solvent-based post-combustion CO₂ capture.This work, developed under the AURORA…
Conference publication – GHGT-17: Viscosity and Density data for the CESAR1 solvent
Abstract Global warming is a major issue that needs to be addressed and limited. The CESAR1 solvent blend has a high potential for becoming a commonly employed, commercial solvent system. In this work, the viscosity and density data for aqueous CO2 loaded CESAR1 (26.6 wt.% AMP 12.8 wt.% PZ) solution…
Conference publication – GHGT-17: “Storage potential evaluation of eastern Mediterranean area as final step of the full chainassessment”
The final step in capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions is geological storage, where CO₂ is injected deep underground into carefully chosen locations. These locations could be natural formations like saline aquifers (underground reservoirs filled with salty water) or empty oil and gas fields.This work, part of the AURORA…
Understanding Solvent Degradation in CO₂ Capture – CESAR1 Solvent Degradation in Pilot and Laboratory Scale
The fight against climate change requires innovative solutions, and one promising method is CO₂ capture and storage (CCS). CCS involves capturing carbon dioxide from industrial emissions before it reaches the atmosphere. At the heart of this process are specialized chemical solvents, such as CESAR1, which absorb CO₂ from flue gases.While…
Turning Waste Into Opportunity: Thermal Reclamation Chemistry of Common Amine Solvents
CO2 capture technology is vital for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. But what happens when the chemicals used in this process wear out or degrade? Scientists have been studying how to rejuvenate these chemicals through a method called thermal reclaiming. This research focuses on ethanolamine (MEA), a widely used solvent for…
Closing Knowledge Gaps – Density and Viscosity of Unloaded and CO2-loaded Aqueous AMP-PZ blends
AURORA’s latest scientific journal publication provides experimental density and viscosity data on different unloaded and CO2-loaded aqueous blends of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) used for absorption-based CO2 capture. The paper also provides correlations for density and viscosity suitable for various modelling works.In our previous review article, we identified knowledge…
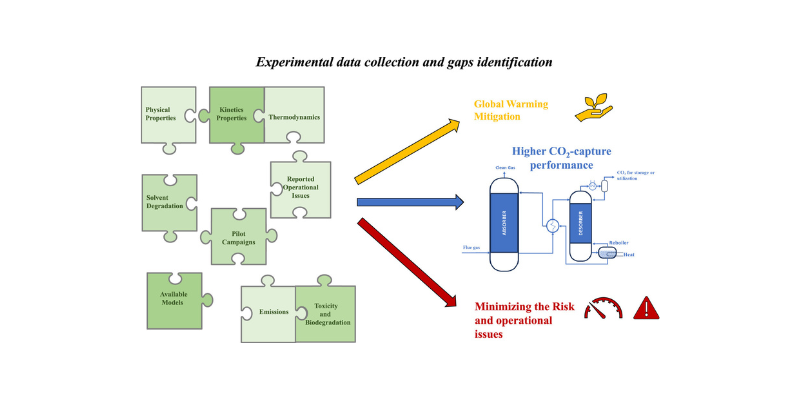
Unlocking New Potential of CESAR1-based chemical absorption Technology: Available data and knowledge gaps of the CESAR1 solvent system
AURORA latest review paper, developed in collaboration with researchers from SINTEF and NTNU, provides a comprehensive analysis of the CESAR1 solvent system. It collects and evaluates existing experimental data, highlights knowledge gaps, and outlines the necessary next steps in research to optimize the use of CESAR1 for CO₂ capture.In the…
Conference publication – Optimal Control of Industrial Solvent-Based CO2 Capture Plants Conference publication
This publication, prepared by our project partners Cybernetica and SINTEF Industry, is a proceeding from the 34th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering and the 15th International Symposium on Process Systems Engineering (ESCAPE34/PSE24), held in Florence, Italy, from June 2-6, 2024.Researchers have developed and tested advanced methods to control…