Abstract
In this work, we developed a new e-NRTL thermodynamic framework for CO2 absorption in aqueous mixtures of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) in Aspen Plus. The e-NRTL AMP/PZ/H2O/CO2 model was fitted on experimental data covering a range of AMP concentration from 12 to 48 mass % and PZ concentration from 2 to 26 mass %, temperature from 20 to 160 °C and CO2 loading from 0 to 1.03 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑂2/𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐴𝑀𝑃+𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑃𝑍. The model predicts the CO2 solubility, as partial pressure of CO2, over aqueous AMP/PZ solutions within an absolute average relative deviation (AARD) of 26.3%, the total pressure of the system with an AARD value of 7.0%, the heat of absorption of CO2 with an AARD value of 10.2%, and the estimated free CO2 concentration with an AARD value of 13.1%. The model gives a good representation of liquid speciation as a function of the CO2 loading and amine concentration. The model shows good predictions of the CO2 solubility over aqueous AMP/PZ solutions at relevant absorber, stripper and water wash amine concentrations and temperatures. The developed e-NRTL model, in combination with mass transfer and CO2 absorption kinetics modeling, is validated with two pilot campaigns: one at the University of Kaiserslautern and one at the Technology Centre of Mongstad. The developed rate-based model predicts the CO2 capture, rich loading, and specific reboiler duty within 5% absolute average relative deviation.
Authors: Diego Morlando, Ying Zhang, Shu Wang, Hanna K. Knuutila.
Publication – Pilot-scale CO2 capture in a cement plant with CESAR1
Abstract Carbon capture from hard-to-abate industries is essential. This study investigates the effect of stripper pressure on the performance of…
New Publication: Aerosol Modeling in CO2 absorption using CESAR1
We are proud to announce that Hallvard F. Svendsen, Hanna K. Knuutila, Ardi Hartono, Maxime Francois and Diego Morlando at…
Thermodynamic Properties of CO₂ Absorption in CESAR1 — Essential Data for Better Process Modelling
We are proud to announce a new scientific publication from the AURORA project, authored by Diego Morlando, Ardi Hartono and…
Journal Publication – In-Depth Study of CESAR1 Solvent Degradation Under CO₂ Capture Conditions
A new scientific publication based on research from the AURORA project has just been released in the journal Industrial &…
Conference publication – GHGT-17: Viscosity and Density data for the CESAR1 solvent
Abstract Global warming is a major issue that needs to be addressed and limited. The CESAR1 solvent blend has a…
Conference publication – GHGT-17: “Storage potential evaluation of eastern Mediterranean area as final step of the full chainassessment”
The final step in capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions is geological storage, where CO₂ is injected deep underground…
Understanding Solvent Degradation in CO₂ Capture – CESAR1 Solvent Degradation in Pilot and Laboratory Scale
The fight against climate change requires innovative solutions, and one promising method is CO₂ capture and storage (CCS). CCS involves…
Turning Waste Into Opportunity: Thermal Reclamation Chemistry of Common Amine Solvents
CO2 capture technology is vital for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. But what happens when the chemicals used in this process…
Closing Knowledge Gaps – Density and Viscosity of Unloaded and CO2-loaded Aqueous AMP-PZ blends
AURORA’s latest scientific journal publication provides experimental density and viscosity data on different unloaded and CO2-loaded aqueous blends of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol…
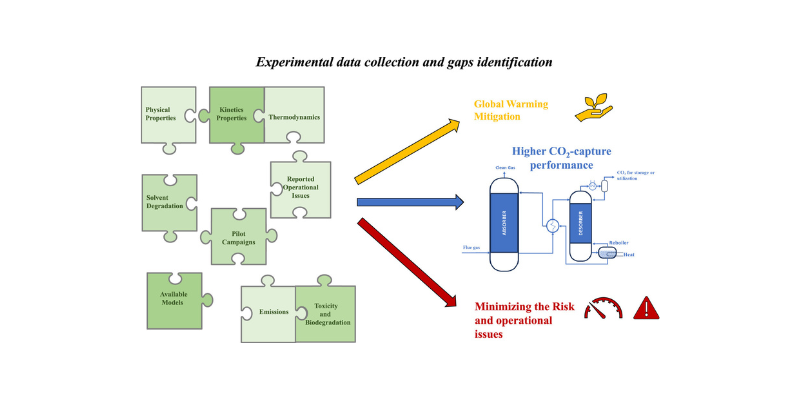
Unlocking New Potential of CESAR1-based chemical absorption Technology: Available data and knowledge gaps of the CESAR1 solvent system
AURORA latest review paper, developed in collaboration with researchers from SINTEF and NTNU, provides a comprehensive analysis of the CESAR1…