AURORA’s latest scientific journal publication provides experimental density and viscosity data on different unloaded and CO2-loaded aqueous blends of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) used for absorption-based CO2 capture. The paper also provides correlations for density and viscosity suitable for various modelling works.
In our previous review article, we identified knowledge gaps related to CESAR1 (aqueous blend of AMP and PZ) solvent system. The review paper identified several gaps in experimental data for CESAR1, including a lack of data related to emissions, solvent stability as well as density and viscosity data for CO2-loaded and unloaded systems.
This new publication addresses the knowledge gap related to density and viscosity of different AMP and PZ blends by providing highly needed data and correlation-based models. .
Why measure the density and viscosity?
The data collected in this work and the correlations developed can be used in developing process models used to design CO2 capture plants. The viscosity impacts the mass transfer between the gas and the liquid phase, i.e. the performance of the absorber and hence the absorber size. Furthermore, the viscosity is also needed in the design of the heat exchangers, while the density of CO2 loaded solutions can be used in online monitoring of the CO2 loading.
The AURORA project will continue the work of closing the knowledge gaps related to the properties of aqueous blends of AMP-PZ.
The work was performed at NTNU by Diego Morlando, Hanna Katariina Knuutila and Ardi Hartono from the Department of chemical engineering at NTNU: https://www.ntnu.edu/chemeng
Understanding Solvent Degradation in CO₂ Capture – CESAR1 Solvent Degradation in Pilot and Laboratory Scale
The fight against climate change requires innovative solutions, and one promising method is CO₂ capture and storage (CCS). CCS involves capturing carbon dioxide from industrial emissions before it reaches the atmosphere. At the heart of this process are specialized chemical solvents, such as CESAR1, which absorb CO₂ from flue gases.While…
Turning Waste Into Opportunity: Thermal Reclamation Chemistry of Common Amine Solvents
CO2 capture technology is vital for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. But what happens when the chemicals used in this process wear out or degrade? Scientists have been studying how to rejuvenate these chemicals through a method called thermal reclaiming. This research focuses on ethanolamine (MEA), a widely used solvent for…
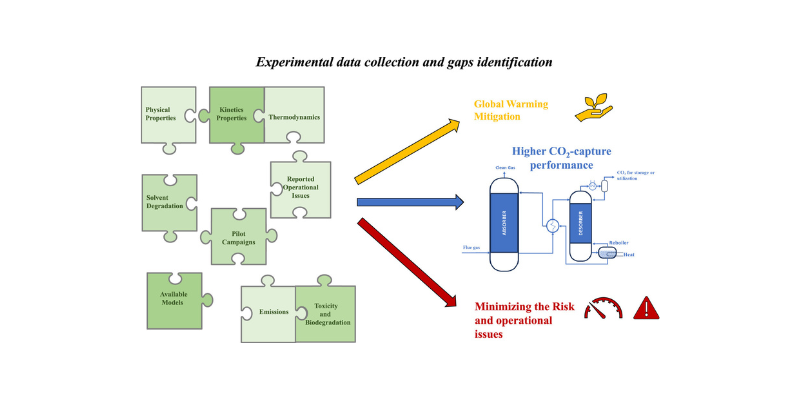
Unlocking New Potential of CESAR1-based chemical absorption Technology: Available data and knowledge gaps of the CESAR1 solvent system
AURORA latest review paper, developed in collaboration with researchers from SINTEF and NTNU, provides a comprehensive analysis of the CESAR1 solvent system. It collects and evaluates existing experimental data, highlights knowledge gaps, and outlines the necessary next steps in research to optimize the use of CESAR1 for CO₂ capture.In the…
Conference publication – Optimal Control of Industrial Solvent-Based CO2 Capture Plants Conference publication
This publication, prepared by our project partners Cybernetica and SINTEF Industry, is a proceeding from the 34th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering and the 15th International Symposium on Process Systems Engineering (ESCAPE34/PSE24), held in Florence, Italy, from June 2-6, 2024.Researchers have developed and tested advanced methods to control…